WHY MEDITATE?
We've heard that meditation can be good for our mind and perhaps we've even felt the calming benefits ourselves, but what's really going on while we sit in silence?
Although the yogis and monks have been practicing meditation for thousands of years, it is only relatively recently that science has begun to study and understand the molecular-level effects of meditation. We are gradually learning how affected molecules are linked to changes in stress responses and mood and the response in the electromagnetic waves of our mind.

HOW DOES MEDITATION REDUCE STRESS?
Mindfulness meditation is shown to decrease our stress response by switching which nervous system in our body is activated. In modern life, we are often in our sympathetic nervous system, which is our fight or flight response. This can be triggered by significant life events or even everyday situations such as increased workload, screen time, frustration in traffic or financial worries. By meditating and concentrating on our breathing our body naturally shifts into our parasympathetic nervous system, which allows us to rest and relax, telling our body that it is okay to slow down. Meditation can shift our brain waves from a higher frequency to a lower frequency, which helps to change how we feel and also stimulate different parts of our brain such as the vagus nerve that help us to slow down and triggers the rest and restore part of our automonic nervous system.
HOW DOES MEDITATION IMPROVE COGNITIVE FUNCTION & SELF AWARENESS?
A study on mindful meditation looked at outcomes six to twelve months after meditating around 20 minutes a day and observed changes in brain structure and function.
Researchers noticed increases in grey matter density in the hippocampus and other frontal regions of the brain as well as increases in anterior insula and cortical thickness. So what does this mean?
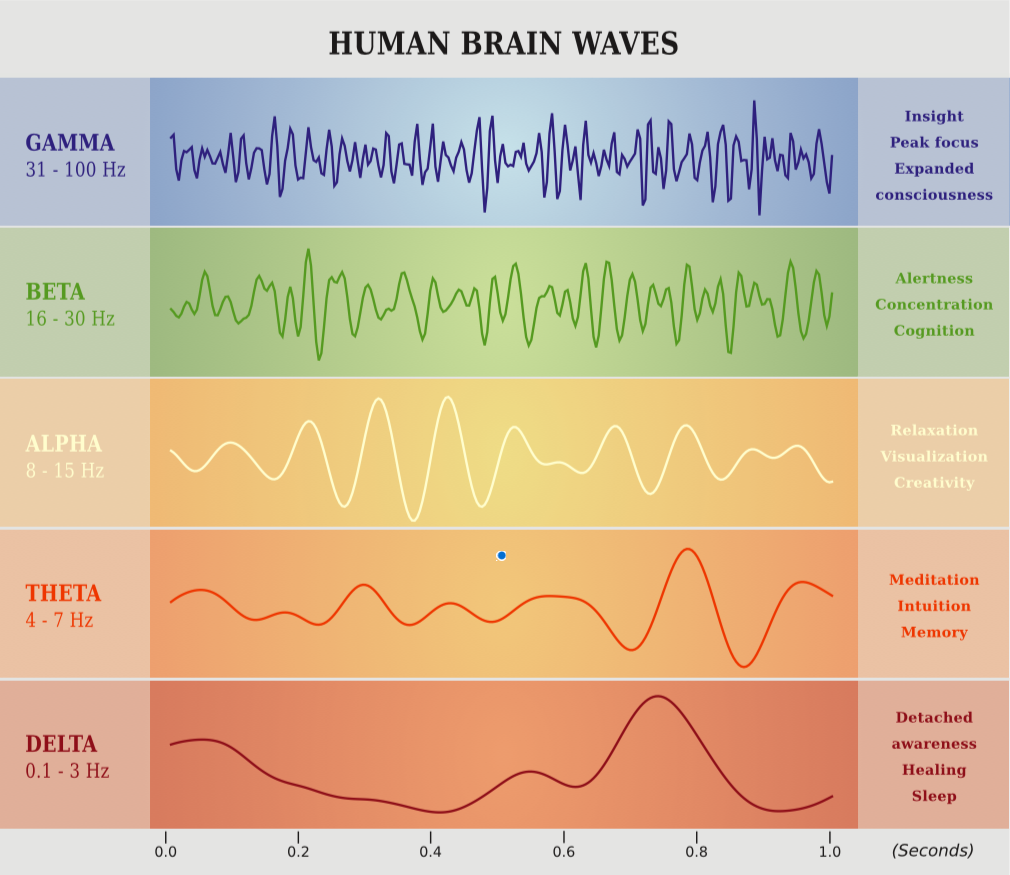
Increases in grey matter and the left hippocampus aid learning, cognition, and memory, resulting in better retention of facts and more mindful behaviour. And increases in the anterior insula and in cortical thickness benefit cognitive function, attention and, self-awareness. There are five types of brain waves, which occur at various frequencies and have different effects on our body and mind which can be influenced by meditation. When we sit to meditate, we will often begin with alpha brain waves and move into a theta state.
HOW DOES MEDITATION MAKE YOU HAPPIER?
Studies show that meditation can significantly affect hormones and neurotransmitters such as cortisol, serotonin, melatonin, and epinephrine. Cortisol is also known as our stress hormone and meditation has proven to lower its levels in our body, making us feel more relaxed and aiding in the transition to our parasympathetic nervous system as mentioned above. Findings also show that regular meditation increases serotonin which is sometimes referred to as our rest and fulfillment hormone. The results of a 2015 study showed that meditation not only increases serotonin levels but also that these levels can remain elevated throughout the day and night, contributing to an overall sense of happiness.
So what are you waiting for? Grab your favourite essential oil blend, put on some calming music and melt into the many benefits that meditation can bring. If you're new to meditation, you can also try our quick 5-minute guided meditation here.





